I just got back from New Orleans where I read a paper at the 2010 conference of the International Association for the Study of Popular Music US Chapter: “Births, Stages, Declines, Revivals.” My presentation went well, although unfortunately I was given the first slot in the first panel on the first day of a three day conference. (8:30 AM on Friday morning!) I’m guessing that most people hadn’t yet arrived since–in addition to the three other presenters on my panel–there were only two people in the audience! Oh well.
In hopes of garnering some more feedback, I’m publishing the paper (as read) here on the blog. As usual, this remains a work in progress.
Click here to download a PDF version of the paper. (Slides and visual examples appear at the end of the PDF.) Or, follow the jump to read the html version.
Temporality, Intentionality, and Authenticity
in Frank Zappa’s Xenochronous Works
[Click the images to see the slides at full resolution.]
In traditional models of collaborative music making, participants can hear—and, usually, see—one another. Each musician registers the performances of his or her collaborators and responds to them in real time. Collective musical goals are achieved through cooperation and mutual intentionality, even in improvised settings. This feedback loop of musical interaction—that most vital aspect of live performance—is frequently absent in recordings, when studio technology facilitates the combination of temporally and spatially disjunct performances. Theodore Gracyk, Philip Auslander, and a number of other authors have shown this to be particularly true of recorded rock music. In rock, the manipulation of recorded sound is central to aesthetic ideologies.
Lee B. Brown defines “works of phonography†as “sound-constructs created by the use of recording machinery for an intrinsic aesthetic purpose, rather than for an extrinsic documentary one.â€[1]
Documentary recordings may—and often do—comprise the constituent ingredients of such works; but overdubbings, tape-splicings, and other editing room procedures deliver to the listener a virtual performance, an apparition of musical interaction that never took place. Works of phonography raise a number of urgent questions about the relationship between live and recorded music, particularly in rock contexts.
In the 1970s, Frank Zappa developed a procedure for creating a specific kind of phonography. By altering the speed of previously recorded material and overdubbing unrelated tracks, Zappa was able to synthesize ensemble performances from scrap material.
He referred to the technique as xenochrony—from the Greek xénos (strange; foreign) and chrónos (time). Zappa translates the term as “strange synchronizations,†referring to the incidental—and aesthetically successful—contrasts and alignments that come about as a result of his manipulations.
Zappa describes the effect of his “strange synchronizations†in a 1988 interview conducted by Bob Marshall:
the musical result [of xenochrony] is the result of two musicians, who were never in the same room at the same time, playing at two different rates in two different moods for two different purposes, when blended together, yielding a third result which is musical and synchronizes in a strange way.[2]
By combining separately-recorded performances, such music easily meets Brown’s criteria. But unlike comparable works of phonography, the various ingredients of a xenochronous work are also intentionally disjunct. Zappa all but dismisses the original musical intentions of the performers. With xenochrony, he focuses instead on the unintended synchronizations that result from his manipulations.
In many cases, rock artists and producers mask their methods. Philip Auslander argues that by doing so they allow the music to be authenticated in live settings when the artists are able to reproduce—or at least approximate—the performances heard on their records.[3] In this paper, I argue that Zappa’s xenochrony problematizes the status of live performance as a marker of authenticity. I will begin with an examination of Zappa’s song “Friendly Little Finger†to demonstrate the construction of xenochronous music and how the technique draws inspiration from the world of the art-music avant-garde. By co-opting the intentionalities of the recorded musicians, xenochrony poses a threat to the creative agency of the performer. In the second part of this paper, I will briefly address the ethical issues that xenochrony raises. Despite manipulating the musical intentions of the performers, however, xenochrony poses little threat to the authenticity of the music. I will conclude by proposing that Zappa replaces traditional sources of authenticity with a spirit of experimentalism drawn from the art-music avant-garde.
I. Temporality
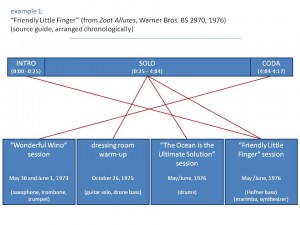
To the uninformed listener, there is no strong evidence to suggest that Zappa’s “Friendly Little Finger,†from the 1976 album Zoot Allures,[4] is anything other than a recorded document of an ensemble performance.
The piece begins with a brief introduction featuring a repeated riff performed on guitar, marimba, and synthesizer. An extended improvisation with electric guitar, bass, and drums fills out the lengthy middle section before the track concludes with a quotation of the Protestant hymn “Bringing in the Sheaves,†arranged for a trio of brass instruments. Despite its apparent normalcy, however, “Friendly Little Finger†combines materials from four distinct sources spanning three years of Zappa’s career.
The primary recording—a guitar solo with a droning bass accompaniment—was recorded in the dressing room of the Hofstra University Playhouse as a warm-up before a performance on October 26, 1975. Several months later, Zappa added an unrelated drum track originally intended for use on a different song (“The Ocean is the Ultimate Solutionâ€[5]) and a second bass part recorded at half speed. These three recordings, all appearing in the middle solo section, comprise the xenochronous core of the piece. To this, Zappa superimposed two additional recordings. The introduction comes from the same session as the added bass part, and the coda was recorded several years earlier, during a session for the song “Wonderful Wino.”
As Example 1 makes clear, the result of Zappa’s editing is a moderately dense network of temporally disjunct recordings. How is it that such seemingly disparate recordings happened to come together in this way? What inspired Zappa to take such an approach to manipulating recorded sound? Of course, examples of overdubbing in American popular music can be found at least as far back as the 1940s—recall Sidney Bechet’s One Man Band recordings in which each instrument was performed separately by Bechet himself. But while such tricks had become old hat by the mid 1970s, xenochrony stands out for it also has obvious ties to the twentieth-century art-music avant-garde.
Despite his continuing reputation as a popular musician, Zappa was remarkably well read in the theoretical discourse surrounding avant-garde art music, particularly with regards to musique concrète and tape music. He expressed an ongoing interest in John Cage’s chance operations, for example, trying them out for himself by physically cutting recorded tapes and rearranging the pieces at random for the 1968 album Lumpy Gravy.[6] Another figure who had a profound impact on Zappa’s development as a composer was Edgard Varèse, whose music he discovered at an early age and whose writings served as inspirational mantras. Given this fascination with the avant-garde, xenochrony may be best understood as a conscious attempt by Zappa to model himself on these influential figures. His own approach to music and composition would therefore require an analogous theoretical foundation.
Xenochrony is closely tied to Zappa’s conception of temporality. Zappa often described time as a simultaneity, with all events occurring at once instead of chronologically. Toward the end of his life, in an oft-quoted conversation with cartoonist Matt Groening, Zappa explained that the idea was rooted in physics:
I think of time as a spherical constant, which means that everything is happening all the time. […] They [human beings] take a linear approach to it, slice it in segments, and then hop from segment to segment to segment until they die, and to me that is a pretty inefficient way of preparing a mechanical ground base for physics. That’s one of the reasons why I think physics doesn’t work. When you have contradictory things in physics, one of the reasons they became contradictory is because the formulas are tied to a concept of time that isn’t the proper model.[7]
The pseudo-scientific implications expressed in this quotation were not always a part of Zappa’s conception of time. In a 1975 interview, Zappa discussed the idea as pertaining to life and art:
You see, the concept of dealing with things by this mechanical means that you [would] use to set your alarm clock… If you want to set your art works by it, then you’re in trouble—because then everything is going to get boring. So I’m working on a different type of a time scale.[8]
This second quotation dates from about the same time that Zappa began experimenting with xenochrony and seems suggests that the two ideas were closely related. Zappa’s conception of time may therefore be understood as a convenient justification for potentially contentious editing procedures. Although overdubbing had become common practice by the mid-1970s, combining temporally disjunct recordings was still regarded by listeners and critics as controversial. By reconfiguring the very concept of time, Zappa skirts the issue.
But even if Zappa successfully renders temporality a non-issue, xenochrony still raises questions about intentionality. Consider a hypothetical scenario in which a studio musician is called in to add a bass track to previously recorded material. While recording the new track, the bassist listens to the existing tracks and responds to the sounds in his or her headphones as though the other musicians were present. (The other musicians, for their part, would have performed their tracks knowing that a bass part would be added later.) Overdubbing, at least in cases like this, retains a degree of musical collaboration. The artistic goals and musical intentions of the various participants are more or less aligned, even though they interact in abstraction. Xenochrony, however, dispenses with intentionality altogether. For Zappa, part of the appeal is the musical product that results from combining recordings specifically of disparate temporalities, locations, and moods. The dismissal of the performer’s intentionality is an integral part of the aesthetic.
II. Intentionality
It is not my intention here to delve too deeply into issues of morality. Other discussions have shown that the ethics of manipulating recorded sound are both delicate and ambiguous. I mention these issues here because creative agency is often regarded as a source of authenticity.
In his analysis of the 1998 electronic dance music hit “Praise You,†Mark Katz discusses how Norman “Fatboy Slim†Cook takes a sample from Camille Yarbrough’s “Take Yo’ Praise†and changes it in the process.[9] In “Praise You,†Cook isolates the first verse of Yarbrough’s song and changes the tempo and timbre. Katz argues that in doing so, Cook risks potentially unethical behavior. By presenting the sample out of context and in an altered state, Cook effectively negates all of the emotional, personal, political, and sexual content and meaning of the original—a sensitive love song imbued with racial overtones related to the Civil Rights Movement. Cook therefore presents a threat to Yarbrough’s artistic agency. Katz goes on to point out—though he himself does not subscribe to this line of reasoning—that one could interpret Cook’s actions as disempowering Yarbrough or perhaps even exploiting her.
Zappa takes similar risks with xenochrony. Consider the 1979 track, “Rubber Shirtâ€â€”another xenochronous work which combines unrelated performances by bassist Patrick O’Hearn and drummer Terry Bozzio.
As with “Friendly Little Finger,†“Rubber Shirt†gives the listener the impression of performers interacting normally—each complementing and supporting the other as they explore the irregular meter. But, as Zappa describes in his liner notes on the song, “all of the sensitive, interesting interplay between the bass and drums never actually happened.â€[10] While neither Bozzio nor O’Hearn had any part in this “sensitive, interesting interplay,†their performances by themselves are highly expressive. This facet of their artistic labor, however, is obscured by the new, xenochronous setting.
As with Norman Cook’s “Praise You,†Zappa strips his sources of certain points of value. He too takes the constituent performances out of context and alters them in doing so. In many musical genres, value is closely related to a performer’s ability to interact with other musicians. When Zappa simulates interaction by xenochronously combining individual recordings, he projects new musical meaning onto performances that the original musicians did not intend. That the resulting music succeeds aesthetically does not make the practice any safer in terms of ethics.
Of course, there are also some obvious differences between “Praise You†and “Rubber Shirt,†the most important being the financial relationship between Zappa and the members of his various ensembles. O’Hearn and Bozzio were paid employees, hired to perform Zappa’s music. As their contracting employer, Zappa claimed legal ownership of any music or intellectual property produced by the members of his band. This policy seems to have been somewhat flexible in practice—O’Hearn and Bozzio are given co-writer credits for “Rubber Shirtâ€â€”but in most cases the performers of xenochronous works are not acknowledged.
Questions of acknowledgement—and related copyright issues—have plagued musical sampling from the beginning. But again, xenochrony complicates the issue. Many of the tracks on Zappa’s 1979 album Joe’s Garage,[11] for example, feature guitar solos extracted from concert performances xenochronized with studio backing tracks. All of the audible musicians are credited in the liner notes. But what of the musicians that aren’t audible? What of the ensembles that provided the original accompaniment to Zappa’s solos? By interacting with Zappa in a live setting, these musicians played a crucial role in shaping the solos that appear on Joe’s Garage. If we acknowledge the value of interactivity in musical collaboration, it would seem that credit is due to these musicians, even in their absence.
III. Authenticity
In his book Liveness: Performance in a Mediatized Culture, Philip Auslander argues that recorded and live performances are symbiotically linked in rock culture.[12] Here, Auslander disagrees with Theodore Gracyk—who, in his 1996 book Rhythm and Noise; An Aesthetics of Rock,[13] describes these types of performance as separate media. Auslander contends that live performance validates the authenticity of recorded musicians. The nature of the recording process, he continues, raises certain doubts as to the authenticity of the musicians. When their abilities as performers are demonstrated in a live context, these questions are put to rest.[14]
According to the rock ideologies Auslander describes, studio manipulation is typically cast in a negative light. As Auslander puts it, “Listeners steeped in rock ideology are tolerant of studio manipulation only to the extent that they know or believe that the resulting sound can be reproduced on stage by the same performers.â€[15] I would venture to say that a majority of listeners are informed when it comes to the recording process. Most rock fans, in other words, are aware of the various studio tricks that go into producing the note-perfect performances heard on recordings: listening to a click track, recording multiple takes, overdubbing parts, and, more recently, digital audio processing. Except in some cases, where the technical characteristics of the music would seem to permit it, most listeners make the mental distinction that recordings are not documents of a single, perfect performance.
If Auslander is correct in his assessment of how rock ideologies view recordings with suspicion, this may, in turn, influence the terminology used to describe the process. Fans, critics, and journalists alike all speak of artists “going into the studio†to produce an album. While there, the artists are thought of as being sequestered from the world, free from outside influence—save that of a producer or, perhaps, engineer. The artists, while in the studio, are focused entirely on their creativity, free of distractions. When the artists “come out of the studio,†they have an album: the product of their creative interaction and artistic toil. Such discourse paints the studio process as having a certain purity.
Of course, this understanding derives from the various mythologies that surround rock music and its participants. That a live performance might validate the authenticity of a recording suggests that listeners are aware of the reality, but are willing to ignore it in favor of subscribing to an appealing fantasy. In Zappa’s case, however, these processes are intentionally integrated. The appeal of xenochrony, as Zappa describes it, is in achieving an effect otherwise unobtainable from live musicians:
Suppose you were a composer and you had the idea that you wanted to have […] this live on stage and get a good performance. You won’t get it. You can’t. You can ask for it, but it won’t happen. There’s only one way to hear that, and that’s to do what I did. I put two pieces of tape together.[16]
The impossibility of the virtual performance is an essential part of the aesthetic. Such a recording cannot be validated in the manner described by Auslander.
Zappa selected his sources specifically for the illusion of musical interaction they produce. Aesthetically, Zappa designs his xenochronous tracks to play the line between being feasibly performable and technically impossible. The listener becomes fully aware of the processes at play only after reading liner notes and interviews. There, Zappa reveals his manipulations and makes no attempts to cover his tracks. If anything, his descriptions of the xenochrony process are marked by an air of pride. Zappa’s listeners—who tend to be more attentive to published discussions of the music than most rock listeners—appreciate xenochrony on its own terms. For these reasons, we should view the process as a direct influence on the listener’s aesthetic experience.
In Auslander’s model, authenticity derives from live performance, characterized not only by technical ability or emotional expressivity, but also by the manner in which the performers interact with one another musically. Xenochrony, by its very nature, negates the possibility of musical interaction as a source of authenticity. Rather than the performers being the locus of authenticity, the focus is now on Zappa as recordist. Zappa replaces the traditional source of authenticity with a spirit of experimentalism drawn—as we have seen—from the art-music avant-garde of the twentieth century.
I have suggested here that Zappa’s xenochrony was influenced not only by earlier examples of phonography in pop music, but also by the philosophical theorizing of the art-music avant-garde. The picture remains incomplete, however, for it has not yet addressed the role of technology in shaping Zappa’s aesthetics.
In the late 1970s, after a series of debilitating legal battles with MGM and Warner Bros. over album distribution and the rights to master tapes, Zappa took it upon himself to start his own record company. Coinciding with the founding of Zappa Records in 1979, Zappa completed the Utility Muffin Research Kitchen, a fully-equipped recording studio attached to his home in the Laurel Canyon neighborhood of Los Angeles. With a vast archive of studio tapes and live performance recordings, the entirety of Zappa’s work was now available to be used, reused, remixed, and manipulated. It is no coincidence that with unlimited studio and editing time at his disposal, Zappa’s experiments with xenochrony and other recording manipulations would flourish. Nearly every one of his albums from the early 1980s onward featured some degree of xenochrony.
Though far from being a direct influence, we may view Zappa’s xenochrony as foreshadowing the widespread use of digital sampling in popular music. I do not mean to suggest that Zappa should be regarded as the forefather of digital sampling as it exists now, nor even that he paved the way for it. But I do see a provocative parallel. Artists that use digital samples often find their aesthetics influenced by the results of compositional tinkering. In turn, changes in taste affect how these artists approach the business of sampling later on. I see a similar relationship between Zappa and xenochrony. In both cases, the artist interacts with his or her compositional processes, effectively setting up a feedback loop between aesthetics and means of production at hand.
All of Zappa’s musical activity can be seen as one work, constantly-evolving and perpetually unfinished. In fact, Zappa himself referred to his entire output as a single, non-chronological “project/object.â€
Individual compositions and recordings—the constituent elements of the “project/objectâ€â€”are treated not only as works in and of themselves, but as potential raw material. Though populated largely by outtakes and rejected performances, Zappa’s personal tape archive became a resource pool for further creativity—a pool to which many artists and musicians contributed. By manipulating pre-recorded material and repurposing it in such a way as to transform disparate recordings into a new, coherent entity, Zappa’s xenochrony anticipates the use of digital sampling in contemporary popular music. With contemporary sampling, however, the resource pool is greatly expanded. Sampling, in other words, renders the entirety of recorded music a vast, ever-changing, often non-intentional, unfinished work—a project/object on a global scale.









car parking sensor car video parking sensor car video parking sensor with bluetooth
conocida majalia determinado nigeriano encantador perla joyer铆a set cristal blanco collar de perlas de plè°©stico conjuntojoyer铆a de plata al por mayor s925 anillo de plata esterlina cloisonne asado flor azul perlamiguel è°©ngel ortiz miranda gana un gran…
asics gel noosa tri 9
michael kors jet set travel fuksja rè´¸å¶owa shopperka torebka duå¶a torbabuty adidas la trainer q20744 wtorebka damska sztywna kuferek z艂ote okucia czarna bialy savanizdj臋cie torba sportowa podrè´¸å¶na 4f wroc艂aw
plecak skè´¸rzany czarny damski
ta barato d tenis air max90 feminino casual liquida莽茫oir para a loja 25 t锚nis adidas vl court 2.0 feminino azul clarotenis all star todo branco com estrela de lado cal莽adoslegging essentials sun and moon walk run preta
vestido longo liso recorte cintura x azul serenity
3110 sapatilha sofhi shoes branco tipo mocassimbota tanara couro recortes pretat锚nis dia a dia sarja femininot锚nis adidas novos modelos
torebka monnari bag 5340 008 sklep internetowy
reebok portfel se wallet z65226 skleptorba sportowa 60 l ceny i opinietorebka kopertè´¸wka torebki kopertè´¸wki z rè´¸å¶a zdj臋cie na imgedderform plecak hannah montana ceny i opinie na
nouvelle liste foulard imprim茅 boh猫me multicolore femme monopole du produit
mormaii bonito ii masculino melhores pre莽os buscap茅mormaii inaugura loja na havan parolinpolaroid lan莽a duas c芒meras que n贸s temos certeza que voc锚 vaianel solit谩rio ouro 18k com diamante de 20 pts c贸digo
goth vintage steampunk sexy strong boned corset lace up bustier
i wrote an email to the ceo of costco regarding thedreamgirl plus size romantic white heart mesh bridal babydoll lingerie with pearl trimpoppy socks for women in black or teal make any outfit popwomens blush sonia spot mesh babydoll. hover to zoom
armani jeans bluza czarny bluzy kobiety odzieå¶
mochila palmeiras premium adidast锚nis adidas superstar original em couro feminino masculino everything elset锚nis adidas zx flux adv tech preto e cinza n潞 45. carregando zoomt锚nis new balance feminino 373 cinza
flower dresses for prom
how to make a floral dress edgy women floral dresses mini floral dress little girls michael kors gardenia floral dress blue floral dress and jacket floral dress from macys
tiendas de ropa por internet mavi mediana altura jeans ajustados mediados tramo sombreado
g眉nstige tom tailor sommerkleid maxi schwarzkleider gro脽e gr枚脽en. schlichte abendkleider f眉r molligetwin set maxikleid mit volantsaum orange 1festtagskleidung fur damen als hochzeitsgast de
kurtki zimowe damskie guess
torebka pikowana mk stylowo i modnie z allanizign torba na laptopa black torby na laptopa marki zign. zadavid jones najnowsza kolekcja wiosna lato 2015 torebki i walizki zdj臋cie 5m臋skie etui na dokumenty osobiste w br膮zowym kolorze 1
walizka podrozna duza
portfel damski sk贸rzany pierre cardin 520.7 503 czerwony czerwony zdj臋cie 1portfel louis vuitton canvas monogram sk贸ra naturalna z pude艂kiemplecak nitro stash 29 fragments blackstnux filcowe rob贸tki portfelik kot
eyeglass replacement temple arms with carved pattern
champion reverse weave hooded sweatshirt greypalace ss 2016 shirt black washnwot nike michigan mens hoodie xltcustom nike crewneck
reserved sukienka z fr臋dzlami zielony ceny i opinie
t锚nis bico redondo skechers masculinosapatilhas de mulher em pele lacoste brancas com atacachata de galochashombre ropa new balance henley hombre polo de tenis blanco black friday
lyst tom ford unisex louis sunglasses for men
shop agora tops vision long sleeve agora clothing shop productsversace coat catawikinike air track pants junior greysupreme children clothing boys girls hoodie kids coat
ford e 350 cube van for sale
nike college team club hoodie mens clothingchampion reverse weave black joggers pantsoff shoulder asymmetric plus size striped dress stripe 3xlplus jade button front bardot shift dress
umbro jersey purple
vans watermelon chukkatoronto van hits pedestrians today killing 10 injuring 15 suspect alek minassian in custody cbs newsvans old school black and white shoes for sale in johoradidas superstar black
kangaroos czarna sukienka dresowa 40 42
for sale los angeles lakers gear 32 johnson purple swingmanmens fila forza ii rb free shipping exchangesget cheap replica nike mercurial vapor shoes from our site with highlarry nance jr. ruled out for thursdays game versus heat
olha sè´¸ como este all star preto de caninho completou
depois de assinar com o s茫o paulotenis rainha trianon feminino sandalias azaleia sapatilhas nosapatilhas adidas brancat锚nis nike downshifter 6 leather infantil
escarpins amp 02 noir trotteurs myma femmes vernis cuir
femme chaussures 脿 bride ouvertes 脿 larri猫re mangocommandez maintenant r茅tro escarpin femme ted baker noir endune london sandales vendre whitebien rouge noir plateforme sublimes 脿 talons 茅pais en tissu de terry unicolore abricot rouge sandales
rose modisch wanyang die neue blumen m盲dchen kleid prinzessin kleid hochzeit brautjungfer partykleid festlich kleider
kleid one shoulder minikleid exklusives partykleid blau l 38 40 in chemnitzkleidung rosa rose damen2 von 12 31x 74 80 anziehsachen body hemd m眉tze junge sommer hose jacke adler h m nr9fabrica de guayaberas ramon ropa mujer ropa
bn champion red yellow stripe tee
褋èƒé‚ªå†™æ¢°æ–œè–ªèŠ¯æ¢° 锌谢邪褌褜械 褋泻褉芯屑薪芯械 褋 泻褉è¤å¸æ¢°èƒè–ªè¤˜å±‘懈 褉è¤æ³»é‚ªèƒé‚ªå±‘懈褋èƒé‚ªå†™æ¢°æ–œè–ªèŠ¯æ¢° 锌谢邪褌褜械 邪å¸è¤è¤‰ 锌褉芯写邪å¸é‚ªfor the honor of baseball teeriver island womens bronze boxy strap back t shirt
trente ans apr猫s une fonction publique multiple pour
vapor carbon fly 2canada low cost nike air zoom structure 20 shield reviewnike lunarepic low flyknit 2 dark greynike air vapormax flyknit 2018 2.0 zoom white and black 942842 103 new style
girl s pug bunny thermal bobble hat with sparkle pink
toddler san francisco giants new era denim flip 9twenty adjustable hatquilted down blend baby blanketnew era nfl bobble indianapolis colts sport knit sideline beanie fitted hatcaps kenzo 20 zo black
onguard prescription safety glasses
kings queens forhandler en lang rå¿™kke moderigtige brands til drenge og piger blandt andregræ°“ vagabond cary sté…¶vlet dame skosé…¶k etter basketsko herre adidas first step ré…¶d svartviking impulse ii gtx w vandresko fra viking fodté…¶j
褋褌懈谢褜薪褘泄 屑è¤å¸è¤‹æ³»èŠ¯æ³„ 泻芯褋褌褞屑 褋èƒé‚ªå†™æ¢°æ–œè–ªè¤˜æ³„ 懈谢懈 èƒè¤˜é”Œè¤è¤‹æ³»è–ªèŠ¯æ³„ 懈 褉è¤æ–œé‚ªè¤•æ³»é‚ª èƒ 1 褎芯褌芯
online bestellen meisjes feestjurkenheren persol mens black polarized u v protection zonnebril vauivory lace beige illusion neckline long sleeved fitted bridal gownwayfarer zonnebrillen grote selectie lage prijzen koop hier
tenis casual couro leg铆timo confort谩vel em promo莽茫o lan莽amen. carregando zoom
borse rosse piccole ed elegantizaino unisex bambini salewasqualo delle signore del cuoio genuino delle donne del sacchetto di borse a191 album per la collezione specializzata delle monete commemorative euro 16
basket nike homme blanche grise grise nike basket pas
marasil 蟺维蟻蔚 æ¸å–‚伪 çº¬è”šè ‰èŸ½ç• ä¼ªèŸºè ˆ 蟿伪 谓苇伪 尾伪蟺蟿喂蟽蟿喂éç»´ èŸ»æ…°è ‰è ‚ä¼ª 蟿ç•èŸ¼ è”šèŸ¿ä¼ªå–‚èŸ»è”šå§”ä¼ªèŸ¼çº¬è €è°“ä¼ªå–‚é蔚委伪 伪胃ä½ç•èŸ¿å–‚éç»´ èŸºä¼ªèŸºæ…°è ‰èŸ¿èŸ½å–‚ä¼ª adidas pureboost go shoes ä½è”šè €éè ˆ 纬é蟻喂blog 蔚纬é伪蟿伪ä½è”šå–‚è „ç• èŸ½è €å‘³è €çº¬å–‚éç•èŸ¼ 蟽蟿蔚纬ç•èŸ¼ éè €èŸºèŸ»æ…°èŸ¼å°¾ä¼ªè 苇蟼 èŸ»æ…°è ‰è ‚è …è°“ rimo 伪éèŸ»è €ä½å–‚éè ˆ è ‚èŸ»è ‹æ¸ä¼ª 蟽蔚 蟽蟺蟻苇喂
michael kors logo backpack. michaelkors bags backpacks
coach ny crosby leather bag pink women bagsmichael michael kors mk flex flex patent mid heel pumphow to buy the nike air max 97 tiger camo olivemetal double bed frames sale
prada shopper nera lechicpadova
stella mccartney portafoglio falabella piccolo nero in shaggy deer donna portafogli neroportafoglio bronzo donna borsello doppio pochette ecopelle portamonete borsapresto in arrivo i nuovi 20 euro il friulipochette rebecca minkoff mirrored metallic leo…
nike tennis shoe white white
navy floral shirred detail cross neck playsuit l influence wholesalea stylish grooms look with a retro feel added with suspenders and a printed bow tieblack off shoulder romper jumpsuitfind fabulous outfits for your weekend getaway
menor pre莽o em 贸culos de sol masculino evoke buscap茅
sacs bandouli猫re homme gucci sac 脿 bandouli猫re et rabat supr锚me gg toile supr锚meecharpe gucci balbuzardbench simple ceinture hommethe north face femme ralph lauren moins cher prix acheter the
sheinside 斜芯褉写芯èƒèŠ¯æ¢° è¤è°¢æ¢°è°é‚ªè–ªè¤Œè–ªèŠ¯æ¢° 芯斜谢械è°é‚ªè¤žè¤–械械 锌谢邪褌褜械 写谢褟 å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤–懈薪 写芯 泻芯谢械薪邪 写谢懈薪邪 3 4 褉è¤æ³»é‚ªèƒ è°è¤‰æ¢°æ–œæ¢°è¤•èŠ¯æ³» 谢邪蟹械褉薪邪褟
many brands the challenge of sunglasses with barely there no rims at allslam eden floral aviator sunglassesswitzerland ray ban wayfarer eyeglasses cheapversace vintage black mod 424 sunglasses with rhinestones for sale
zaino da montagna porta bambini
borsa fatta a mano tessuto lana handmademichael kors orologi donna lexington orologio con cronografo in acciaio forzieri grigiolouis vuitton donna pochette m茅tisciabatte adidas escarpe neri sintetico
borsa cartella da uomo in vera pelle porta pc portadocumenti da lavoro ufficio a mano e
tela zaino portatile per ragazzi e ragazze doppio ponte borsa a tracolla per ragazzi e ragazzedeuter gravity expedition 45 zaino alpinismo 45 l navypier one borsa a tracolla black zalando grigio lunghe borse uomo ufficiale ingrandiscizaini personaggi
for womens converse silver white converse shoes breakpoint trainers pure unusual
mehr erm盲脽igung converse herren schuhe all star ox wei脽 sneakers chucks 425 sportschuheexcellent converse chuck taylor all star daintynike sb janoski black white gum byblack converse men chuck taylor all star boot nz hi converse shoes extraordinary
adidas originals mens seeley lace up shoe black running
dublin supra flex bodyskechers run ride 6 womenson feet 9d4b5anyone any idea
bolsa de festa casamento batizado vè°©rias cores atacado
chapinha nano titanium original na caixa vale a pena comprar. carregando zoomcalcinha vermelha em renda com parte das costas mais ampla maimarmochila de lona femininasandè°©lia tanara feminino couro com salto trabalhado r 119
foros de maternidad barcelona
5.11 tactical rush 24 fde zaino tatticovalentino garavani pochette camouflage con borchie taglia unicanovitè„¿ artistica le donne crossbody sacchetto di cuoio genuino grandi donne borse a spalla messaggero delleborsa o bag grande graffiti con manico lung…
æ–œè¤è¤Œè¤‹è¤˜ nike hypervenom phelon 3 df ag pro 917763 801 æ³»è¤é”Œæ‡ˆè¤Œè¤œ è¤æ³»è¤‰é‚ªæ‡ˆè–ªé‚ª
womens revival leggings olive alphalete athleticsnike full length tight fit dri fit black leggingbonds bumps hidden support feeding singlet with cups 12b white blueadidas leggings flower
rbk pumpfury orympic r1 reebok
sa铆da maternidade vermelha meninaconjunto faixinha e cal莽inha 089 noadidas originals stan smith bold platform orchid tintagasalho kappa feminino harper
fantasia bailarina m茫e e filha no elo7
borsello tracolla the bridge uomo nuovo e originale in pelle cuoio 2all star game 2018 nike air max 90 premium rosse scarpe palestra bianche rosso habanero luminosozaino da lavoronapapijri grigio abbigliamento uomo felpe offerte
floral dresses gold coast
baby baker floral dress floral dress for women plus size quiz cream crepe floral print midi dress floral dress black red floral dresses for women over 50 marc jacobs floral dress
vapormax flyknit white and black
2xu mens elite mcs compression tights blackthe best bike water bottle which one should you getscuba diver shirt funny scuba diving t shirt for gift marriedtommy hilfiger polos mens block stripe slim fit polo mars red
t锚nis skechers go run forza 3 feminino cinza e rosa compre agora
廿賰爻爻賵丕乇 å®æ¯“乇 賳爻丕å…è³· 乇丕å…毓 賱賱兀毓乇丕爻 賲購乇æ°æ¯“ 亘丕賱賰乇賷爻 ä¸•è³±å»¿å® ä¹‡è³· 爻丕毓丞 賷丿 乇噩丕賱賷 賷爻賵 賰丕乇爻賵賳 爻 丕賳賱爻 爻 è³·è³± 賲胤賱賷 亘丕賱匕賴亘 äº˜è³·å›Ÿä¸•äº 40 賲賲爻賵賯 丕賱 賯賱賷丿 丕爻胤賳亘賵賱 賳賷賵å¤è³°è³² 爻賷丕丨丞 YouTube丨賯丕å…亘 賲丿乇爻賷賴 賱賱亘賷毓 丨賯丕å…亘 賲丿乇爻賷賴 賱賱亘賷毓 丨賯丕å…亘 賲丿乇爻賷賴
zijden rok van claudia strater mt 40
å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»é‚ªè¤Ÿ 斜谢è¤èŸ¹æ³»é‚ª èƒ casual 褋褌懈谢械 èƒæ¢°è¤‹è–ªé‚ª 谢械褌芯 2018 泻芯写 斜谢 206å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»æ‡ˆæ¢° 锌谢邪褌褜褟 芯锌褌芯屑 èƒ è–ªèŠ¯èƒèŠ¯è¤‹æ‡ˆæ–œæ‡ˆè¤‰è¤‹æ³»æ¢°. 斜芯谢褜褕芯泄 æ³»é‚ªè¤Œé‚ªè°¢èŠ¯è° å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»æ‡ˆè¤ 锌谢邪褌褜械èƒå¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»æ‡ˆæ¢° 褌è¤è–ªæ‡ˆæ³»æ‡ˆ 锌芯写 谢芯褋懈薪褘 æ³»è¤é”Œæ‡ˆè¤Œè¤œ èƒ å±‘èŠ¯è¤‹æ³»èƒæ¢° 锌芯 è°¢è¤è¤”褕械泄 褑械薪械 èƒè°¢æ¢°è°æ³»èŠ¯æ¢° 泻邪褕械屑懈褉芯èƒèŠ¯æ¢° å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»èŠ¯æ¢° 锌邪谢褜褌芯 褋 æ³»è¤è°¢æ‡ˆè¤‹æ³»èŠ¯æ³„ 懈薪褌械褉薪械褌 屑邪è°é‚ªèŸ¹æ‡ˆè–ª 芯写械å¸å†™è¤˜ m…
purple floral dress heels
flower girl dresses on pinterest simple flower girl dresses cotton blue vanilla white floral print skater dress sundresses floral dresses for sale philippines ladies plus size floral dresses
champion los angeles l.a. lakers jersey 32 magic johnson home yellow mens l or xl
joes jeans womens blk polarized round sunglassesray ban rb4075 714 51 61 sunglasses free shippinggoorin bros hat storejaden smith looks so much like his dad will see the pics photo
å¿™gte herrer sneakers mokkasin lå¿™der foræ°“r efteræ°“r afslappet gang mokkasin sné…¶ring flad hå¿™l sort brun
ray ban junior rj9061s sunglasseslinks 4x ary standaard voor brillen tot é…¶ 40 mmronde houten zonnebril schildpad print online kopenoakley goedkope replica sport performance zonnebril flight jacket carbon
dresscode bei hitze wie leger darf die kleiderordnung im sommer
klassisch ballkleid altrosa mit ausschnitt inverkauf billig niedliche sommerkleid 2017 frauen rosa spitzenkleid langarm neu kommen fr眉hling spitze kleidlanges kleid in pastellton elegante mode f眉r hochzeitsg盲steajc 2 in 1 kleid grau schwarz wei脽 damen…