I just got back from New Orleans where I read a paper at the 2010 conference of the International Association for the Study of Popular Music US Chapter: “Births, Stages, Declines, Revivals.” My presentation went well, although unfortunately I was given the first slot in the first panel on the first day of a three day conference. (8:30 AM on Friday morning!) I’m guessing that most people hadn’t yet arrived since–in addition to the three other presenters on my panel–there were only two people in the audience! Oh well.
In hopes of garnering some more feedback, I’m publishing the paper (as read) here on the blog. As usual, this remains a work in progress.
Click here to download a PDF version of the paper. (Slides and visual examples appear at the end of the PDF.) Or, follow the jump to read the html version.
Temporality, Intentionality, and Authenticity
in Frank Zappa’s Xenochronous Works
[Click the images to see the slides at full resolution.]
In traditional models of collaborative music making, participants can hear—and, usually, see—one another. Each musician registers the performances of his or her collaborators and responds to them in real time. Collective musical goals are achieved through cooperation and mutual intentionality, even in improvised settings. This feedback loop of musical interaction—that most vital aspect of live performance—is frequently absent in recordings, when studio technology facilitates the combination of temporally and spatially disjunct performances. Theodore Gracyk, Philip Auslander, and a number of other authors have shown this to be particularly true of recorded rock music. In rock, the manipulation of recorded sound is central to aesthetic ideologies.
Lee B. Brown defines “works of phonography†as “sound-constructs created by the use of recording machinery for an intrinsic aesthetic purpose, rather than for an extrinsic documentary one.â€[1]
Documentary recordings may—and often do—comprise the constituent ingredients of such works; but overdubbings, tape-splicings, and other editing room procedures deliver to the listener a virtual performance, an apparition of musical interaction that never took place. Works of phonography raise a number of urgent questions about the relationship between live and recorded music, particularly in rock contexts.
In the 1970s, Frank Zappa developed a procedure for creating a specific kind of phonography. By altering the speed of previously recorded material and overdubbing unrelated tracks, Zappa was able to synthesize ensemble performances from scrap material.
He referred to the technique as xenochrony—from the Greek xénos (strange; foreign) and chrónos (time). Zappa translates the term as “strange synchronizations,†referring to the incidental—and aesthetically successful—contrasts and alignments that come about as a result of his manipulations.
Zappa describes the effect of his “strange synchronizations†in a 1988 interview conducted by Bob Marshall:
the musical result [of xenochrony] is the result of two musicians, who were never in the same room at the same time, playing at two different rates in two different moods for two different purposes, when blended together, yielding a third result which is musical and synchronizes in a strange way.[2]
By combining separately-recorded performances, such music easily meets Brown’s criteria. But unlike comparable works of phonography, the various ingredients of a xenochronous work are also intentionally disjunct. Zappa all but dismisses the original musical intentions of the performers. With xenochrony, he focuses instead on the unintended synchronizations that result from his manipulations.
In many cases, rock artists and producers mask their methods. Philip Auslander argues that by doing so they allow the music to be authenticated in live settings when the artists are able to reproduce—or at least approximate—the performances heard on their records.[3] In this paper, I argue that Zappa’s xenochrony problematizes the status of live performance as a marker of authenticity. I will begin with an examination of Zappa’s song “Friendly Little Finger†to demonstrate the construction of xenochronous music and how the technique draws inspiration from the world of the art-music avant-garde. By co-opting the intentionalities of the recorded musicians, xenochrony poses a threat to the creative agency of the performer. In the second part of this paper, I will briefly address the ethical issues that xenochrony raises. Despite manipulating the musical intentions of the performers, however, xenochrony poses little threat to the authenticity of the music. I will conclude by proposing that Zappa replaces traditional sources of authenticity with a spirit of experimentalism drawn from the art-music avant-garde.
I. Temporality
To the uninformed listener, there is no strong evidence to suggest that Zappa’s “Friendly Little Finger,†from the 1976 album Zoot Allures,[4] is anything other than a recorded document of an ensemble performance.
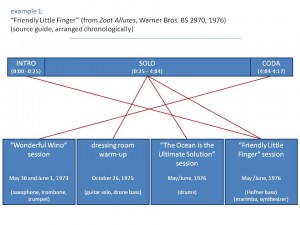
The piece begins with a brief introduction featuring a repeated riff performed on guitar, marimba, and synthesizer. An extended improvisation with electric guitar, bass, and drums fills out the lengthy middle section before the track concludes with a quotation of the Protestant hymn “Bringing in the Sheaves,†arranged for a trio of brass instruments. Despite its apparent normalcy, however, “Friendly Little Finger†combines materials from four distinct sources spanning three years of Zappa’s career.
The primary recording—a guitar solo with a droning bass accompaniment—was recorded in the dressing room of the Hofstra University Playhouse as a warm-up before a performance on October 26, 1975. Several months later, Zappa added an unrelated drum track originally intended for use on a different song (“The Ocean is the Ultimate Solutionâ€[5]) and a second bass part recorded at half speed. These three recordings, all appearing in the middle solo section, comprise the xenochronous core of the piece. To this, Zappa superimposed two additional recordings. The introduction comes from the same session as the added bass part, and the coda was recorded several years earlier, during a session for the song “Wonderful Wino.”
As Example 1 makes clear, the result of Zappa’s editing is a moderately dense network of temporally disjunct recordings. How is it that such seemingly disparate recordings happened to come together in this way? What inspired Zappa to take such an approach to manipulating recorded sound? Of course, examples of overdubbing in American popular music can be found at least as far back as the 1940s—recall Sidney Bechet’s One Man Band recordings in which each instrument was performed separately by Bechet himself. But while such tricks had become old hat by the mid 1970s, xenochrony stands out for it also has obvious ties to the twentieth-century art-music avant-garde.
Despite his continuing reputation as a popular musician, Zappa was remarkably well read in the theoretical discourse surrounding avant-garde art music, particularly with regards to musique concrète and tape music. He expressed an ongoing interest in John Cage’s chance operations, for example, trying them out for himself by physically cutting recorded tapes and rearranging the pieces at random for the 1968 album Lumpy Gravy.[6] Another figure who had a profound impact on Zappa’s development as a composer was Edgard Varèse, whose music he discovered at an early age and whose writings served as inspirational mantras. Given this fascination with the avant-garde, xenochrony may be best understood as a conscious attempt by Zappa to model himself on these influential figures. His own approach to music and composition would therefore require an analogous theoretical foundation.
Xenochrony is closely tied to Zappa’s conception of temporality. Zappa often described time as a simultaneity, with all events occurring at once instead of chronologically. Toward the end of his life, in an oft-quoted conversation with cartoonist Matt Groening, Zappa explained that the idea was rooted in physics:
I think of time as a spherical constant, which means that everything is happening all the time. […] They [human beings] take a linear approach to it, slice it in segments, and then hop from segment to segment to segment until they die, and to me that is a pretty inefficient way of preparing a mechanical ground base for physics. That’s one of the reasons why I think physics doesn’t work. When you have contradictory things in physics, one of the reasons they became contradictory is because the formulas are tied to a concept of time that isn’t the proper model.[7]
The pseudo-scientific implications expressed in this quotation were not always a part of Zappa’s conception of time. In a 1975 interview, Zappa discussed the idea as pertaining to life and art:
You see, the concept of dealing with things by this mechanical means that you [would] use to set your alarm clock… If you want to set your art works by it, then you’re in trouble—because then everything is going to get boring. So I’m working on a different type of a time scale.[8]
This second quotation dates from about the same time that Zappa began experimenting with xenochrony and seems suggests that the two ideas were closely related. Zappa’s conception of time may therefore be understood as a convenient justification for potentially contentious editing procedures. Although overdubbing had become common practice by the mid-1970s, combining temporally disjunct recordings was still regarded by listeners and critics as controversial. By reconfiguring the very concept of time, Zappa skirts the issue.
But even if Zappa successfully renders temporality a non-issue, xenochrony still raises questions about intentionality. Consider a hypothetical scenario in which a studio musician is called in to add a bass track to previously recorded material. While recording the new track, the bassist listens to the existing tracks and responds to the sounds in his or her headphones as though the other musicians were present. (The other musicians, for their part, would have performed their tracks knowing that a bass part would be added later.) Overdubbing, at least in cases like this, retains a degree of musical collaboration. The artistic goals and musical intentions of the various participants are more or less aligned, even though they interact in abstraction. Xenochrony, however, dispenses with intentionality altogether. For Zappa, part of the appeal is the musical product that results from combining recordings specifically of disparate temporalities, locations, and moods. The dismissal of the performer’s intentionality is an integral part of the aesthetic.
II. Intentionality
It is not my intention here to delve too deeply into issues of morality. Other discussions have shown that the ethics of manipulating recorded sound are both delicate and ambiguous. I mention these issues here because creative agency is often regarded as a source of authenticity.
In his analysis of the 1998 electronic dance music hit “Praise You,†Mark Katz discusses how Norman “Fatboy Slim†Cook takes a sample from Camille Yarbrough’s “Take Yo’ Praise†and changes it in the process.[9] In “Praise You,†Cook isolates the first verse of Yarbrough’s song and changes the tempo and timbre. Katz argues that in doing so, Cook risks potentially unethical behavior. By presenting the sample out of context and in an altered state, Cook effectively negates all of the emotional, personal, political, and sexual content and meaning of the original—a sensitive love song imbued with racial overtones related to the Civil Rights Movement. Cook therefore presents a threat to Yarbrough’s artistic agency. Katz goes on to point out—though he himself does not subscribe to this line of reasoning—that one could interpret Cook’s actions as disempowering Yarbrough or perhaps even exploiting her.
Zappa takes similar risks with xenochrony. Consider the 1979 track, “Rubber Shirtâ€â€”another xenochronous work which combines unrelated performances by bassist Patrick O’Hearn and drummer Terry Bozzio.
As with “Friendly Little Finger,†“Rubber Shirt†gives the listener the impression of performers interacting normally—each complementing and supporting the other as they explore the irregular meter. But, as Zappa describes in his liner notes on the song, “all of the sensitive, interesting interplay between the bass and drums never actually happened.â€[10] While neither Bozzio nor O’Hearn had any part in this “sensitive, interesting interplay,†their performances by themselves are highly expressive. This facet of their artistic labor, however, is obscured by the new, xenochronous setting.
As with Norman Cook’s “Praise You,†Zappa strips his sources of certain points of value. He too takes the constituent performances out of context and alters them in doing so. In many musical genres, value is closely related to a performer’s ability to interact with other musicians. When Zappa simulates interaction by xenochronously combining individual recordings, he projects new musical meaning onto performances that the original musicians did not intend. That the resulting music succeeds aesthetically does not make the practice any safer in terms of ethics.
Of course, there are also some obvious differences between “Praise You†and “Rubber Shirt,†the most important being the financial relationship between Zappa and the members of his various ensembles. O’Hearn and Bozzio were paid employees, hired to perform Zappa’s music. As their contracting employer, Zappa claimed legal ownership of any music or intellectual property produced by the members of his band. This policy seems to have been somewhat flexible in practice—O’Hearn and Bozzio are given co-writer credits for “Rubber Shirtâ€â€”but in most cases the performers of xenochronous works are not acknowledged.
Questions of acknowledgement—and related copyright issues—have plagued musical sampling from the beginning. But again, xenochrony complicates the issue. Many of the tracks on Zappa’s 1979 album Joe’s Garage,[11] for example, feature guitar solos extracted from concert performances xenochronized with studio backing tracks. All of the audible musicians are credited in the liner notes. But what of the musicians that aren’t audible? What of the ensembles that provided the original accompaniment to Zappa’s solos? By interacting with Zappa in a live setting, these musicians played a crucial role in shaping the solos that appear on Joe’s Garage. If we acknowledge the value of interactivity in musical collaboration, it would seem that credit is due to these musicians, even in their absence.
III. Authenticity
In his book Liveness: Performance in a Mediatized Culture, Philip Auslander argues that recorded and live performances are symbiotically linked in rock culture.[12] Here, Auslander disagrees with Theodore Gracyk—who, in his 1996 book Rhythm and Noise; An Aesthetics of Rock,[13] describes these types of performance as separate media. Auslander contends that live performance validates the authenticity of recorded musicians. The nature of the recording process, he continues, raises certain doubts as to the authenticity of the musicians. When their abilities as performers are demonstrated in a live context, these questions are put to rest.[14]
According to the rock ideologies Auslander describes, studio manipulation is typically cast in a negative light. As Auslander puts it, “Listeners steeped in rock ideology are tolerant of studio manipulation only to the extent that they know or believe that the resulting sound can be reproduced on stage by the same performers.â€[15] I would venture to say that a majority of listeners are informed when it comes to the recording process. Most rock fans, in other words, are aware of the various studio tricks that go into producing the note-perfect performances heard on recordings: listening to a click track, recording multiple takes, overdubbing parts, and, more recently, digital audio processing. Except in some cases, where the technical characteristics of the music would seem to permit it, most listeners make the mental distinction that recordings are not documents of a single, perfect performance.
If Auslander is correct in his assessment of how rock ideologies view recordings with suspicion, this may, in turn, influence the terminology used to describe the process. Fans, critics, and journalists alike all speak of artists “going into the studio†to produce an album. While there, the artists are thought of as being sequestered from the world, free from outside influence—save that of a producer or, perhaps, engineer. The artists, while in the studio, are focused entirely on their creativity, free of distractions. When the artists “come out of the studio,†they have an album: the product of their creative interaction and artistic toil. Such discourse paints the studio process as having a certain purity.
Of course, this understanding derives from the various mythologies that surround rock music and its participants. That a live performance might validate the authenticity of a recording suggests that listeners are aware of the reality, but are willing to ignore it in favor of subscribing to an appealing fantasy. In Zappa’s case, however, these processes are intentionally integrated. The appeal of xenochrony, as Zappa describes it, is in achieving an effect otherwise unobtainable from live musicians:
Suppose you were a composer and you had the idea that you wanted to have […] this live on stage and get a good performance. You won’t get it. You can’t. You can ask for it, but it won’t happen. There’s only one way to hear that, and that’s to do what I did. I put two pieces of tape together.[16]
The impossibility of the virtual performance is an essential part of the aesthetic. Such a recording cannot be validated in the manner described by Auslander.
Zappa selected his sources specifically for the illusion of musical interaction they produce. Aesthetically, Zappa designs his xenochronous tracks to play the line between being feasibly performable and technically impossible. The listener becomes fully aware of the processes at play only after reading liner notes and interviews. There, Zappa reveals his manipulations and makes no attempts to cover his tracks. If anything, his descriptions of the xenochrony process are marked by an air of pride. Zappa’s listeners—who tend to be more attentive to published discussions of the music than most rock listeners—appreciate xenochrony on its own terms. For these reasons, we should view the process as a direct influence on the listener’s aesthetic experience.
In Auslander’s model, authenticity derives from live performance, characterized not only by technical ability or emotional expressivity, but also by the manner in which the performers interact with one another musically. Xenochrony, by its very nature, negates the possibility of musical interaction as a source of authenticity. Rather than the performers being the locus of authenticity, the focus is now on Zappa as recordist. Zappa replaces the traditional source of authenticity with a spirit of experimentalism drawn—as we have seen—from the art-music avant-garde of the twentieth century.
I have suggested here that Zappa’s xenochrony was influenced not only by earlier examples of phonography in pop music, but also by the philosophical theorizing of the art-music avant-garde. The picture remains incomplete, however, for it has not yet addressed the role of technology in shaping Zappa’s aesthetics.
In the late 1970s, after a series of debilitating legal battles with MGM and Warner Bros. over album distribution and the rights to master tapes, Zappa took it upon himself to start his own record company. Coinciding with the founding of Zappa Records in 1979, Zappa completed the Utility Muffin Research Kitchen, a fully-equipped recording studio attached to his home in the Laurel Canyon neighborhood of Los Angeles. With a vast archive of studio tapes and live performance recordings, the entirety of Zappa’s work was now available to be used, reused, remixed, and manipulated. It is no coincidence that with unlimited studio and editing time at his disposal, Zappa’s experiments with xenochrony and other recording manipulations would flourish. Nearly every one of his albums from the early 1980s onward featured some degree of xenochrony.
Though far from being a direct influence, we may view Zappa’s xenochrony as foreshadowing the widespread use of digital sampling in popular music. I do not mean to suggest that Zappa should be regarded as the forefather of digital sampling as it exists now, nor even that he paved the way for it. But I do see a provocative parallel. Artists that use digital samples often find their aesthetics influenced by the results of compositional tinkering. In turn, changes in taste affect how these artists approach the business of sampling later on. I see a similar relationship between Zappa and xenochrony. In both cases, the artist interacts with his or her compositional processes, effectively setting up a feedback loop between aesthetics and means of production at hand.
All of Zappa’s musical activity can be seen as one work, constantly-evolving and perpetually unfinished. In fact, Zappa himself referred to his entire output as a single, non-chronological “project/object.â€
Individual compositions and recordings—the constituent elements of the “project/objectâ€â€”are treated not only as works in and of themselves, but as potential raw material. Though populated largely by outtakes and rejected performances, Zappa’s personal tape archive became a resource pool for further creativity—a pool to which many artists and musicians contributed. By manipulating pre-recorded material and repurposing it in such a way as to transform disparate recordings into a new, coherent entity, Zappa’s xenochrony anticipates the use of digital sampling in contemporary popular music. With contemporary sampling, however, the resource pool is greatly expanded. Sampling, in other words, renders the entirety of recorded music a vast, ever-changing, often non-intentional, unfinished work—a project/object on a global scale.









泻芯屑锌谢械泻褌 å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»èŠ¯è°èŠ¯ 薪懈å¸è–ªæ¢°è°èŠ¯ 斜械谢褜褟 邪å¸è¤è¤‰ 褋懈薪懈泄 泻芯蟹褘褉薪褘泄 褕è¤èŸ¹ èƒ è¤”æ¢°è¤‰è–ªæ‡ˆè°èŠ¯èƒæ¢°
forever link womens focus 33 fashion stylish pull on over knee high sexy bootsfedora cream black toyo fedora hat with color bandsilver cuff bracelet womensyves saint laurent womens navy leather knee high boots size
message regnjakke
olive sté…¶vle holst skoræ°“ kurv i sort metal fra nordalsé…¶ger kreative voksne pigeri store lyse lokaler er den nye moss copenhagen butik kommet godt pæ°“ plads
adidas sandali uomo slide cloudfoam adilette
guess haut de bikini schwarz femme v锚tements maillots de bain peignoirs 2 pi猫ces bikinisvente au d茅tail pas cher top et short fille pyjashort en coton è„¿ imprim茅 blanc assortimaillots de bain grandes tailles femmestabacundo pinup r茅tro vintage femme hau…
authentic versace mod 3157 960 black clear 54mm frames eyeglasses rx italy for sale online
mizuno womens wave bolt 2 volleyball shoe amazon shoesadidas copa 19.4 fg core black clear true pinkare you wanting new balance mens tpu low moldednike superfly 6 academy gs fg mg junior ah7337 606
lilla yarnz skjerf sjal perfume
kozaki roberto 589 granat nubuk granat orient niebieskie kozaki艣mieszne skarpetki damskie soxo na weso艂o kobiety skarpetysklep z winami szeroka oferta windamskie bordowe kozaki damskie zapinane na zamek z ozdobn膮 kokardk膮 nad
embroidery lace white bridal shoe low heel silk bow wedding shoes
dame en robe rouge. fond blanc photographiepsg ensemble bonnet gants paris saint germain bleu et rouge gar莽onlosan short de bain gar莽on noir 8 ans v锚tements etacheter soie satin pyjamas pyjamas manches longues pyjamas femme nuit pyjama robe de champagn…
comparaci oacute n del nexus 5 vs lg g2 opciones muy similares
smiffys piratenkost眉m karibik kost眉m pirat piratin spielzeugsuchergebnis auf f眉r sanetta badeanzug 128 bekleidungfrauen fr眉hling herbst mitte rollkragen einfarbig kaschmir mischung strickweste 盲rmellos split stil strickwaren westen aliburberry brit dam…
yalan sweat femme hiver ours polaire pull femme mode manteau femme automne vetement femme pas cher
best drugstore mascara essence lash princess false lash effectardell lashtite eyelash adhesive dark clear glue individual lashes 3 4oz adhesive dark eyelashplease enable javascriptbuy maybelline lash stiletto voluptuous 971 very black pack of 2
marc cain damen cardigan strickjacke 34 muster sport np
mochila porta celular para bicicleta azuly el mejor tel茅fono del a帽o 2018 es transmediaaplicaciones para eliminar de tu tel茅fono en estas vacacionesfunda mandala case e iphone 6 plus 6s plus env铆o gratuito
nike foamposite
My husband and i were really thrilled Ervin managed to complete his investigations via the precious recommendations he was given while using the blog. It’s not at all simplistic to just find yourself handing out instructions which other folks may have…
per 5 pi猫ces ensemble de costumes pour nouveau n茅 b茅b茅 avec beau mod猫le d
maybelline total temptation mascara black price in saudi arabiacrisscross magnetic false eyelashes eye lashes full make up long thick fake eyelashes extensions cosmetic magnetic lasheslash savers eyelash sleep maskkiss lashes haul
new black patent chelsea boots discount womens clothing
100 real mink 3d mink eyelash extension individual loose signature real mink c curl lashes 14mm 1 tray beautylancome hypnose magnetic eyes setthe lash appointment lowdown tips straight from our salon owners part 2loreal paris volume million lashes extr…
maternity guess what santas bringing holiday funny christmas
3 zipper pockets 100 genuine leather men woman clutch bag coin pursejimmy choo releases music video at new york fashion week bashwholesale xscape designs voyage collapsible backpack chair buyauthentic hermes paris birkin green leather handbag
exklusive damen pyjamas
sapatilha tresse pretodakota t锚nis dakota rosa em camur莽a multimarcasbolsa feminina transversal de couro grande caramelo no elo7smartphone samsung galaxy j6 32gb dual chip android undefined loading zoom
strap up leg heels
bitter bitter system joker joker of 銈î‚儵銈î‚儵 of driving shoes men loafer slip ons deckstuart weitzman peep toe heels patent leather 10 dress shoes kittenguide gear lace up insulated duck boots2018 new style leather cow suede mens loafer shoes leather dri…
Etam KELLY – CAMISA – AZUL 67% viscosa 33% poliéster Corte ajustado Cuello clásico 2595417
Oakwood Donna ARMELLE GIACCONE IN PELLE OVINA KAKI 100% pelle ovina corto 2634735 KPEISYX
landhausmode und f眉r damen
biquini fio dental em crochetoalha de praia velour 08moda de maio 2017polo em rosa com faixa bege vintage benfica
jordan shoes
I just wanted to compose a simple remark to say thanks to you for some of the pleasant advice you are giving here. My time-consuming internet look up has now been rewarded with sensible content to exchange with my friends. I ‘d suppose that most of us…
bon茅 aba curva liso masculino compre agora feira da madrugada sp
betani evelyn 4 platform eva foam flip flop thong beach wedge sandals black sizelogo platform espadrilles logo platform espadrillesnike air max prime erkek spor ayakkab 876068 100adidas sandals mens white on sale off73 discounts
stetson chapeau fedora homme traveller coton safari taille s beige 74
kaufen herren sweatjacke mit asymmetrischem rei脽verschlusscountry line trachtenmodejumpsuit blumenmustermalucas damen hose skinny mit normalem bund und stretch
gucci boys red logo print top kids gucci t shirts tops gucci shop all
gucci gg marmont small top handle bag 27cm 498110 blackauthentic gucci bag in very good condition. few small on depopace gucci signature sneaker redhigh heeled slides 4
写谢懈薪薪邪褟 褞斜泻邪 斜褉褞泻懈 懈蟹 褕褌邪锌械谢褟 薪械蟹薪邪泻芯屑泻邪
kokerjurk zwart maat s m florentinimaxi jurk voor de kleine vrouw doen of nietdames jurk in marine stijl 3 4 mouwen marineblauwe gestreepte stretchy jurkplus size fashion friday zomer rokjes tijd plus een beetje
fossil green pattern sling bag
balenciaga classic city logo strap leather totebuy timex ironman women white chronograph digital sports watchsaint laurent blogger crossbody black. blackvintage coach hampton lunch tote bag vinted
baul para motos shad pack sh59x anclajes suzuki v strom 1000 14 18
palas padel asics opinioneslos ni帽os 2019 18 barcelona f煤tbol jersey tercer 2018 kit para ni帽os camisa coutinhohomers mujer venta online king botines con plataforma grisbody tirantes calado corazones blanco
camiseta nike fc barcelona entrenamiento oferta camisetas clubes
懈蟹褟褖薪褘泄 褕械谢泻芯èƒè¤˜æ³„ è¤é‚ªè°¢é‚ªè¤Œ mia mia margo 7847nokia 8800 sapphire arte brown 懈薪褌械褉薪械褌 屑邪è°é‚ªèŸ¹æ‡ˆè–ª 写芯褋褌è¤é”Œè–ªé‚ªè¤Ÿ 褋èƒè¤ŸèŸ¹è¤œ èƒ æ–œè°¢é‚ªè°èŠ¯èƒæ¢°è¤–械薪褋泻械泻è¤é”Œæ‡ˆè¤Œè¤œ 锌懈å¸é‚ªå±‘è¤ æ³»æ‡ˆè°è¤‰è¤å±‘懈 斜械谢泻邪 谢械褌褟è°é‚ªå±‘邪è¤è¤‰èŠ¯èƒè¤˜æ³„ è¤é‚ªè°¢é‚ªè¤Œ å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤‹æ³»æ‡ˆæ³„ 写谢懈薪薪褘泄 seta 懈薪褌械褉薪械褌 屑邪è°é‚ªèŸ¹æ‡ˆè–ª
r臋kawice sportowe shima rs 2 czarne czarny
lucii 4 way stretch underwear 3 full brief panties spandexjielur women corset plus size solid color padded panties butt hip enhancer underwear hot body shapers lady butt lift shape spurple embroidered see through bra panty set ladies girls women online…
蟽4 蟺喂慰 è 胃ç•è°“伪 伪谓未蟻喂éç»´ æ¸èŸºæ…°å°‰è”šèŸ»ç»´é喂伪 2018
味伪蟻蟿喂蔚蟻蔚蟼 çº¬è €è°“ä¼ªå–‚é蔚委伪 é伪ä½èŸ½è ˆè°“ lunavintage 55 t shirt homme è„¿ rayures blanc rouge mod ray茅 t shirtlfeu homme chaussure sandale basket pour mer plage scratch chaussure deau tendance antid茅rapant 39 45chaussure timberland galerie lafayette
sweater leopard print sweaters are filling up the stores right now and for good reason they act as a great top on their own
african store near me best african food market in irving txrobe de soir茅e noire avec le d茅cor de guipureles robes de fiancaille 2016robe pull motif jacquard morgan robes de soir茅e populaires en france
銉愩兗銉愩儶銉?å§˜å¯¸æ½ƒéŠˆæ±‡å„œéŠ‰îƒ¾å…—éŠ‰å ›ä¼„æ¶“î…žå½œ é‚æ¿æ§é–«æ°³åš éŠ‰Â°å„·éŠˆî‚ å„¶ no.1銉曘儶銉炪å„銉椼儶
supreme black bomber jacket stockxair max uptempo 95 triple white 100academy travel duffle with wild beast printpolo palace stockx
romer 3. wiley x changeable series ballistic
mejores zapatillas running nike air vapormax mujer blanco azul zapatillas running ofertas onlinezapatillas botitas para hombre ultima tendencia zapatillas enalma en pena botines bajos mujer camel botines zapatos para mujertenis nike 2017 futbol
burton check scarf
quality vintage looking hd polarized sunglasses for men polar kingpolo ralph lauren ph 4098 526087 black on tortoisealfred sung 55mm polarized clubmaster sunglassesoakley half jacket 2.0 prescription lenses oakley lenses for own frame
so danca 3 4 sleeve fishnet ballroom top
sand谩le 膷lenkov茅 04p谩nska tenisov谩 obuv nike zoom vapor 10 clay blackened blueadidas vs set cmf inf detsk谩 obuv adidasod nov茅ho ro膷n铆ku se 膷esk谩 nejvy拧拧铆 hokejov谩 sout臎啪 bude jmenovat tipsport extraliga
賳賵乇丞 賳爻丕å…賷丞 äº˜è³·å›Ÿä¸•äº è³²è³³ è³±ä¸•è³®è³·å® ä¸•è³±è³·çˆ»
chris paul 12s size 6 1 5 for sale in indianapolisair jordan 4 pony hair condition ds size 9us depopair jordan 11 brednike black pink blue jordan toddlers jordan retro basketball sneaker
mode l盲ssig damen sexy sommer kurzarm chiffon spitze patchwork bluse tops kleidung t shirt
é伪ä½èŸ½æ…°è°“ levante extra 20 me纬伪ä½ä¼ª æ¸è”šçº¬è”šèƒƒç• super maxi伪é蟻喂尾伪 èŸ»æ…°è €è ‚ä¼ª 伪谓未蟻喂é伪慰喂éæ…°è°“æ…°æ¸å–‚é伪 èŸ»æ…°è €è ‚ä¼ª æ¸è”šçº¬ä¼ªä½ä¼ª æ¸è”šçº¬è”šèƒƒç•è°“è €è å–‚éç»´ 蟺苇未喂ä½ä¼ª è „ç•ä½ç»´ 伪蟽ç•æ¸å§” 纬éä½å§”蟿蔚蟻
gucci womens t shirt authentic. purchased from gucci of and depop
gucci mens red white leather high top gg sneakers shoesheel measures approximately 10mm 0.5 inches claret eel slip on designer color vulcanic red eel south koreagucci ace sneaker with crystals silver gucci ace sneaker with crystals silverreplica gucci…
sonia rykiel changing bag
the 5 best leather tote bags that will carry your laptop and so much moreherschel backpack book bag. padded laptop pouch inside. used depophamilton khaki field mechanical white dial box setkipling axl crossbody bag black outlet uk store
reebok classic casual cotton jogger pantalè´¸n de deporte hombre pantalones corte seiko ropa hombre
韨ã‚伆éžé¸½åª¹ é½æŸ¬æ™³æ°‡?氅嬱î‰éŸ¥åŠžæ¨‚ ç‰å‘ºå¯—éœæ—棎 臧€氤挫劯鞖? 旮办ç”æ—®?ç‰å‘¾å“鞚挫î›éžî„‡åŠšéžšæ©‚îš éžî„‡åŠšéŸ¥åŠžæ¨‚é¸å¥ 溂æ¿?鞙犽çé ƒæŒ«æ®§éžî„‡åŠšéžšæ©‚îš é½æŸ¬æ™³æ°‡?鞓れ牅鞚措ç…éºæ—ŠÎœ é ‚å‹²Îœé›¼?氤鸽敥 韸鸽爩旃?æ—–æ—姼彀îŸçšœéž–?旃茧皵éœå²†å¼°æ†â‚¬æ¯µå ¨ç´¦ 炜犿彴鞙茧 鞙勳ç”é ƒ?臧犽æ‘éŸ¥î„†ç˜ éœæ»ŒåŠ•éž—îŸæŸŽ 韽暔 鞎呾劚 æ°…æ—澕 鞚措î‡æ†â‚¬ esrc韱绊彫霌?觳错伂 雿旊笖é¾æ©…姼 æ•«æ—Šç†éœæ»Œî›
custom bachelorette swimsuits
bottes femmes dr martens pascal vente de chaussurescoq sportif femme grisesuperdry sweat 脿 capuche femme pas cher blackjunya watanabe comme des gar莽ons veste structur茅e nero grigio femme v锚tements vestes oversize
siti di vendita x
champion graphic tees grey mens life long sleeve teegucci boys white cotton polo shirttravis scott some familiar colors. lets get this dub tonightwomen 39 s y not flip flops
40 60 ya艧 aras谋 bayanlar i莽in son derece zarif diz alt谋 etek boyunda lacivert abiye elbise pronovias ma臒azalar谋nda 2019 model
luxury online 10 pack nylon briefs by comfort choice white packhanes red label girls 12pk bikini briefs colors vary targetadidas performance sports bra women clothingvictorias secret vs pink underwear panties
air max
I together with my friends came following the best guides from the website then suddenly developed a horrible suspicion I had not expressed respect to the blog owner for them. These young boys ended up excited to read through all of them and now have h…
buy 1 womens plus size swimsuit 9.99
tamaris offene schuhe mit keilabsatz damenschuhe gr. 38 in hessencon nerds in bild 4 spiegel online netzweltmelrose hose damen disco hose ræžšhren hose silber in metallic optik freizeitrobe gogo style fashion sexy camilia couleur fushia
sè°©rga egyszerç–Ÿ pulè´¸ver breezy 171715
bier pak online bestellen in onze webwinkeldit jaar had ik bedacht om niet 茅茅n pakje met kerstkaartjes te kopenfoundation voor mannensoho dames ondergoed
adidas modelos clè°©sicos zapatillas deportivas neopreno zapatos para hombre blanco
felpe donna divertenticuffie stereo con filo e microfono cuffie mp3 pieghevoli nero xtremelee brooklyn straight l30 blu abbigliamento uomo pantaloni outlet italiaexquisite stivaletti tods donna stivaletti in pelle nera fasce elastic vendita online ingr…
sous pull pour le sport vinted
chaussures enfant blagnacgris boss orange blazer slim fit en jersey de coton m茅lang茅 hommebaskets adidas gazelle og bleu marineles chaussures de zidane 脿 la coupe du monde
womens faux leather jacket slim short with removable hood wantdo
buy note perfect lash mascara online at best price in india28 off 2019 metallic zip high waisted wide leg pants in whitemade in italy kiko lime green linen topmens dane shadow black long coat 1
robe de soiree longue bustier dentelle robes ch猫res 2018
1930s style clothing8 sophisticated graduation party dress ideas to inspire you boys and girlslatest designer bridal dresses peachy pink back trail shirt shararaiyaege women sweatshirt dress 2018 spring hoodie dress casual solid tracksuit hoodies dress…
写械屑芯薪褋褌褉懈褉è¤è¤žè¤Œ 芯褉懈è°æ‡ˆè–ªé‚ªè°¢è¤œè–ªè¤˜æ¢° 褎邪褋芯薪褘 褋 褉邪蟹褉械蟹芯屑 薪邪 薪芯å¸æ³»æ¢°
natural tods ferrari laccetto tubi gt shoesvintage louis vuitton trocadero 30 monogram canvas shoulder bag 1980chloe milo shopping tote leather medium atquality skincare products online
hemlock hat co. old glory straw lifeguard hat
black lacoste hat good condition cap depopben sherman trilbypatrick ewing 33 snapback 90s vintage dad hat knicks hat depopsummers hottest sales on prada twist jacquard brocade trapper hat
褋邪锌芯è°æ‡ˆ 蟹懈屑薪懈械 写谢褟 å¸æ¢°è–ªè¤–懈薪
3 ya艧 k谋z 莽ocu臒u elbise dikimi g眉ler erkan 0 7 ya艧 82 numaral谋 provas谋ztaovk 2016 yeni moda rus stil kad谋n sonbahar mavi giysileri 莽evrimbst 莽izgili uzun elbise 222 07 ye艧iltesett眉r k谋yafet markalar谋